The Wonder Years: Exploring Growth Milestones
Watching a child grow is an intricate combination of numerous developmental factors. The growth trajectory encompasses not just noticeable physical changes, but also critical cognitive and emotional leaps.
Physical Development and Its Influences
A child's physical development is influenced by a blend of innate genetics and environmental factors. This includes nutrition, which plays a significant role in determining when and how children achieve developmental milestones. While genetics set the stage, the environment, including dietary habits and social settings, can significantly affect growth patterns. For instance, the timing of puberty can be swayed by nutritional variables and socioeconomic conditions. A well-fed child often has a more predictable developmental course compared to those facing nutritional adversities. The connection between nutrition and perinatal factors—conditions and care during pregnancy and early childhood—is critical. Parental knowledge about nutrition and health care directly affects a child’s physical development and resilience against early childhood ailments.
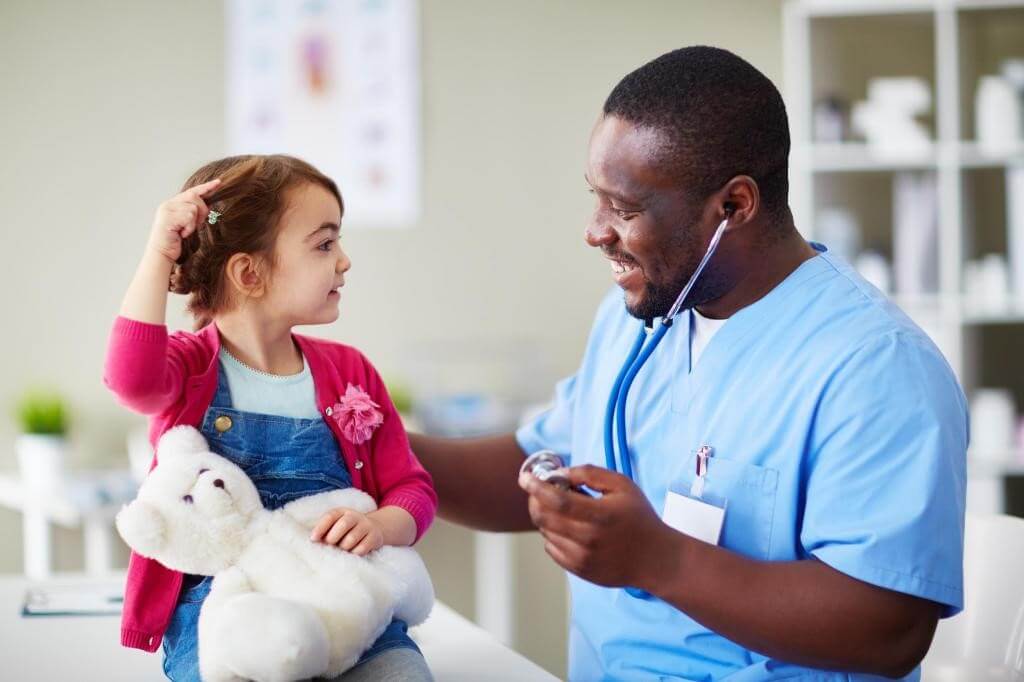
The Role of Health Monitoring
Children requiring more specialized monitoring, such as those with cardiac or pulmonary conditions, benefit from advanced medical insights. Innovations in diagnostics—like the use of biomarkers—offer clinicians vital information about treatment efficiency and disease progression, allowing for personalized medical care. These developments ensure that children with special health needs receive personalized assistance promptly, thereby significantly enhancing their potential to achieve their developmental milestones. This level of personalized care also opens avenues for interventions that can dramatically improve quality of life and developmental outcomes.
Socio-Environmental and Emotional Factors
Beyond the physical realm, a child’s developmental environment is pivotal in shaping cognition and emotion. Children with neurodevelopmental variations, like autism or ADHD, particularly benefit from equitable and informed support structures. Emotional well-being of caregivers is equally crucial, as their stability and resilience directly affect a child’s sense of security and development. Ensuring that caregivers, teachers, and healthcare providers are supported fosters a nurturing environment for the child. Ultimately, a child’s emotional and mental health are anchored by the ecosystem of support they receive, emphasizing the importance of fostering environments that bolster overall growth and development.
Growing Minds: The Link Between Nutrition and Learning
Nutrition's impact goes beyond physical health, extending deeply into cognitive development and emotional balance.
Fueling Young Minds: Nutrition's Role in Cognitive Development
The brain's development is reliant on a consistent supply of essential nutrients, which serve as building blocks. From infancy through the school years, each bite of food provides the resources needed for cognitive tasks—memory, concentration, and learning. Iron, for example, is indispensable for brain oxygenation, while zinc plays a crucial role in neural communication. Calcium contributes not only to strong bones but also to nerve signaling. As we understand more about the gut-brain connection, the importance of holistic nutrition becomes clearer. Prebiotics and other gut-supporting foods have been shown to influence mood and cognitive performance, highlighting the importance of nutritional choices for developmental health.
How Nutrients Shape Learning and Attention
Diet shapes not only physical health but also cognitive abilities. A diet rich in balanced nutrients aids in maintaining stable energy levels necessary for concentration and attention. Vitamins, especially the B-group, are critical to brain energy processes, while magnesium supports various biochemical reactions, including those critical to learning and memory. Thus, ensuring sufficient intake of these nutrients paves the way for better academic performance and cognitive endurance. Arranging meals to include complex carbohydrates provides a steady energy release, preventing sugar crashes that can disrupt focus and learning.
The Brain's Connection to Food and Memory
Food experiences shape brain development and preferences. Positive associations with healthy foods promote lifelong healthy eating habits. Encouraging diverse diets early creates a positive framework, reducing the risk of malnutrition-related cognitive deficits and fostering better cognitive outcomes. As children repeatedly encounter healthful foods, they form a resilient mental foundation supported by positive neurological associations. This understanding encourages practices that help create an environment where children can grow into adults with robust health and cognitive capabilities.
Building Emotional Resilience: Key Strategies for Youth
Developing emotional resilience is vital for handling life’s challenges. Fostering this resilience equips children with the tools to remain stable amid stress and uncertainty.
Building Emotional Strongholds: Key Strategies for Mental Resilience
Building resilience involves practical skills, supportive environments, and emotional awareness. Introducing concrete actions, such as relaxation techniques, helps children navigate adversity. Techniques like breathing exercises can restore calm in stressful moments, teaching children self-regulation. Grounding exercises, which refocus attention, offer simple yet effective coping methods. These practices empower children by demonstrating that self-control over emotions is attainable, equipping them to handle stress effectively.
The Power of Knowledge and Connection
In fostering emotional resilience, emotional literacy is key. Teaching children to recognize and articulate emotions demystifies them, making feelings manageable and less intimidating. Skills like empathy and cooperation further support social and emotional development. Adults model these traits through attentive listening and validating children’s feelings, illustrating that seeking support is strength, not a weakness. Sharing these skills builds a robust emotional toolkit, essential for healthy relationships and emotional well-being.
Creating Supportive Environments
Stable environments foster resilience. Regular routines and open communication create a security net, allowing children to explore and thrive. Supportive responses to errors and failures teach children that challenges foster growth and learning. These nurturing settings inspire confidence and provide a safe base for children to venture into the world, encouraging exploration and growth.
Guided Practice and Modern Support
Modern resources, like interactive stories or mindfulness apps, make learning emotional regulation engaging. These tools provide structured opportunities to practice coping mechanisms, reinforcing lessons from caregivers and educators. Children confronted with emotional challenges learn to navigate them through engaging formats, bolstering their confidence and independence in managing emotions. With technological guidance and support, children develop competencies in emotional self-management.
Community Influence: Immunity and Mental Health in Children
Childhood wellness rests on nurturing immunity and mental health, crucially influenced by both community support and early interventions.
Decoding Pediatric Immunity: The Invisible Shields of Childhood
Understanding pediatric immunity centers on how protective systems develop and shield children. A newborn’s immediate immunological defense comes from maternal antibodies received in utero. This temporary, passive immunity offers crucial early protection while the child’s immune system develops its defenses. Immunizations further enhance this process by safely exposing the immune system to prepare for potential future threats. Community immunity, or herd immunity, exemplifies how collective immunization efforts fortify a community’s resilience against diseases.
Mental Health Strategies: Nurturing Young Minds
Mental health nurture begins early. Integrated mental health services in schools eliminate barriers to access, ensuring deteriorating mental health is addressed timely. Encouraging supportive environments at home and school, alongside regular screenings, ensures intervention before severe issues arise. Programs fostering mental health literacy and resilience can curb the increasing prevalence of anxiety and depression in youth.
| Topic | Key Insights | Source Institution | Publication Date |
|---|---|---|---|
| Child Development | Early cognitive and emotional development is crucial for long-term mental health; interventions in early years improve outcomes. | National Institute of Child Health and Human Development (NICHD), USA | 2023-08 |
| Early Learning | Quality early learning programs enhance school readiness and social skills; disparities exist based on socioeconomic status. | UK Department for Education | 2023-11 |
| Adolescent Behavior | Behavioral health challenges in youth often emerge during adolescence; programs targeting resilience reduce risk behaviors. | Australian Institute of Family Studies | 2024-02 |
| Nutrition For Children | Balanced nutrition supports physical growth and brain development; micronutrient supplementation reduces anemia and cognitive delays. | Public Health England | 2023-09 |
| Mental Health In Youth | Increasing prevalence of anxiety and depression in youth; integrated mental health services in schools improve access and outcomes. | Canadian Pediatric Society | 2024-01 |
| Pediatric Immunity | Vaccination coverage improvements linked to decreases in infectious diseases; immune system development critical in first years. | Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), USA | 2023-12 |
This table highlights the intersection of various developmental aspects, shedding light on the importance of early interventions and community support in nurturing healthy, resilient youth.
Bridging Education and Holistic Wellness
Education’s evolution into a holistic ecosystem underscores the importance of comprehensive child development approaches.
Beyond ABCs: Integrating Wellness in Early Education
Shifting educational practices to emphasize wellness involves recognizing that emotional and physical states impact learning. Incorporating proactive wellness strategies in education, such as open communication and tailored interventions, helps build a foundation of health from the onset. By intertwining wellness into educational frameworks, children acquire habits that promote lasting health and academic success.
The Power of Partnership: A Community-Wide Approach
Holistic well-being requires collaboration between schools, health institutions, and families. Through partnerships, resources are pooled, enhancing support systems for children. Collaborations across sectors improve educational strategies and health services, providing comprehensive care that supports the entire child. Such collaborations ensure equitable access to health and educational resources.
Building Blocks for Resilience: Skills Beyond the Classroom
Modern education emphasizes practical skills critical for navigating life’s complexities. Teaching effective communication, decision-making, and resilience within school programs equips children to manage adversity and interpersonal relationships effectively. Life skills education, paired with values instilled by family and community, enables children to take charge of their well-being and grow into self-assured, proactive adults. By embedding these principles into education, we cultivate a generation prepared for the dynamic world ahead.
Question and Answer
-
What are some key factors that influence child development during the early years?
Early child development is influenced by a combination of genetic, nutritional, environmental, and emotional factors. Nutrition plays a crucial role, as a balanced diet supports physical growth and cognitive development. Environmental influences, such as a child's home life and access to educational resources, significantly affect learning and social skills. Emotional well-being, fostered by supportive relationships and stable environments, is essential for building resilience and mental health.
-
How can nutrition impact a child's cognitive development and mental wellness?
Nutrition is fundamental to a child's cognitive development and mental wellness. Essential nutrients like iron, zinc, and omega-3 fatty acids contribute to brain function and development. Iron is vital for oxygen transport to the brain, while omega-3 fatty acids are crucial for brain structure and function. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports cognitive functions such as memory, attention, and problem-solving, ultimately fostering a child's emotional and mental health.
-
What role does adolescent behavior play in child development, and how can it be managed?
Adolescent behavior is a critical aspect of child development, marked by significant physical, emotional, and social changes. Managing this behavior involves understanding developmental milestones and providing appropriate guidance. Encouraging open communication, setting clear expectations, and promoting healthy peer relationships are vital strategies. Additionally, fostering independence while providing supportive boundaries helps adolescents navigate challenges and develop into well-adjusted adults.
-
Why is pediatric immunity important, and how can it be supported?
Pediatric immunity is crucial as it protects children from infections and diseases during their developmental years. A child's immune system can be supported through vaccinations, which prepare the body to fight specific infections. A balanced diet rich in vitamins and minerals, regular physical activity, adequate sleep, and good hygiene practices also strengthen immunity. Educating parents about the importance of these factors ensures that children have a robust immune foundation.
-
What strategies can be implemented to support mental health in youth?
Supporting mental health in youth involves creating a safe and nurturing environment that promotes emotional well-being. Strategies include encouraging open communication, teaching stress management techniques, and providing opportunities for physical activity, which can enhance mood and reduce anxiety. Schools and communities can offer programs that foster social connections and teach resilience skills. Access to mental health resources and professionals ensures that children receive necessary support when facing emotional challenges.