Riding the Autonomous Wave: How Self-Driving Vehicles are Changing the Commute
The daily commute for millions is set to evolve dramatically with the advent of autonomous vehicles. No longer just imaginative creations in sci-fi novels, these self-navigating cars are slated to revolutionize our interactions with roads and vehicles alike. This evolution encompasses a spectrum of exciting possibilities but also presents significant hurdles needing careful navigation.
A New Vision for Daily Travel
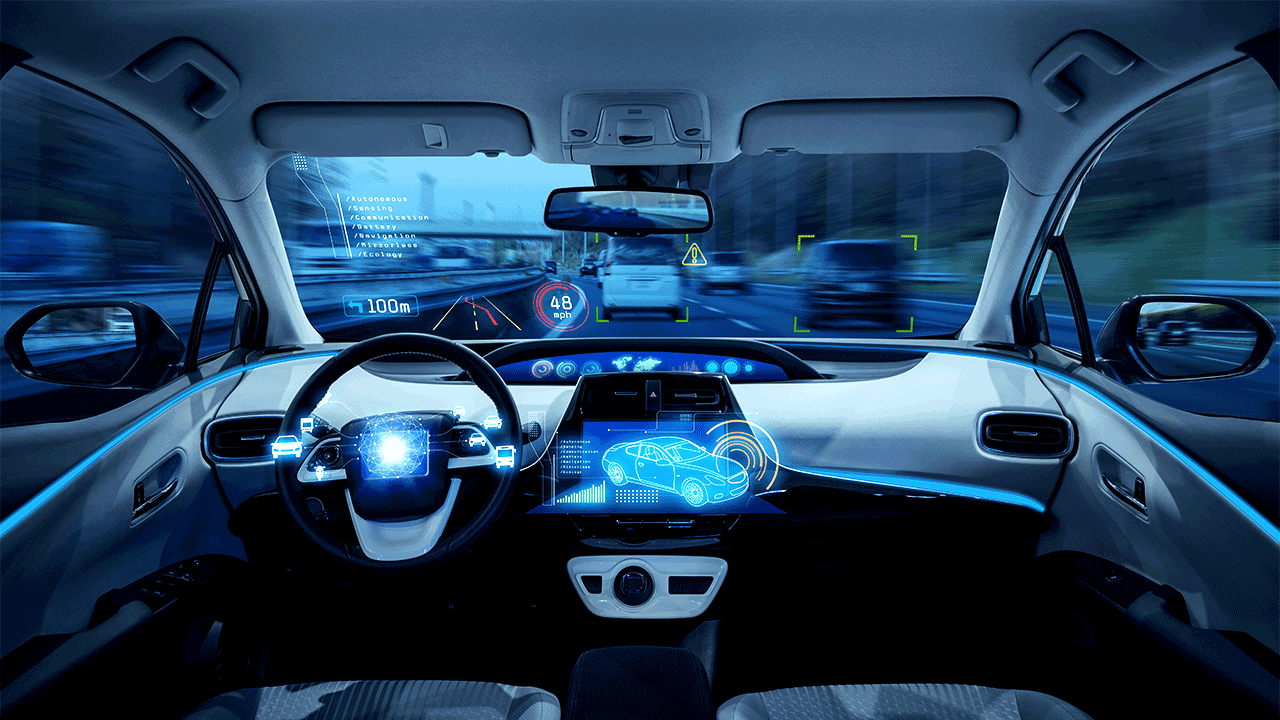
Autonomous vehicles promise to redefine personal travel with enhanced safety and efficiency. Remarkably, many traffic incidents are rooted in human oversight—be it distraction, fatigue, or misjudgment. Self-driving cars, armed with an array of sensors, boast constant vigilance, enabling them to react swiftly and accurately, potentially reducing accident rates significantly. Their capacity to mitigate human error could transform our roads into safer realms for all, encompassing not just drivers and passengers but also pedestrians and cyclists.
Increased efficiency is another crucial promise of autonomous technology. Imagine smoother traffic flow where self-driving vehicles negotiate optimal speeds and spacing, collectively reducing congestion. This collaborative driving minimizes the stop-and-go nature of current traffic systems, resulting in quicker travel times and decreased fuel consumption. This is particularly impactful for electric self-driving cars, which offer zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to cleaner urban air.
Furthermore, by entrusting driving to technology, travel time can become a period of personal enrichment. Vehicles transform into spaces for relaxation or productivity—a mobile office, a quiet reading corner, or even a family cinema. The hours previously lost in traffic can instead enhance personal and professional lives.
Navigating the Roadblocks: Reality Meets the Road
Realizing the vision of an autonomous future is fraught with challenges. Although advanced, the technology behind autonomous vehicles continues to mature. Navigating the unpredictable chaos of real streets presents complexities far surpassing those on test tracks. Current systems, though sophisticated, can falter under unusual conditions like severe weather, confusing markings, or erratic human behaviors. The path toward near-perfect reliability demands comprehensive testing and refinement.
Public trust is equally critical. For most, relinquishing control of a vehicle requires a leap of faith. High-profile incidents impact perception, creating skepticism. Building public confidence hinges on a transparent track record of safety combined with regulations that keep pace with rapid technological advancements. Questions of liability in accidents pose further complications—whether responsibility lies with the owner, car manufacturer, or software developer remains ambiguous. A clear, fair legal framework is essential to advance autonomous technology from concept to everyday reality.
Redefining the Journey: Benefits for People and Society
The advent of self-driving technology brings with it profound shifts beyond mere technology, touching people's daily routines and societal operations. These changes promise personal convenience, improved lifestyle quality, and transformative impacts on urban environments.
A New Era of Personal Mobility
The most immediate individual benefit of autonomous technology is reclaimed time, turning a once stressful commute into a productive or enjoyable experience. For individuals unable to drive due to age or disability, autonomous vehicles provide newfound freedom, enabling access to employment, healthcare, and social interactions independently. This inclusivity extends beyond personal convenience to urban design; such precision in vehicle management could enhance parking efficiency, transforming urban spaces into parks or housing.
Autonomous networks also herald smarter cities by optimizing traffic management systems. Today's traffic inefficiencies often stem from inconsistent human driving. By harmonizing vehicle movement and intent, self-driving technology promises smoother flows devoid of unnecessary braking. This innovation offers cleaner, efficient urban environments, aligning with efforts to create sustainable, resilient cities.
The Foundation: Infrastructure and Integration
Realizing the full potential of autonomous mobility requires a dual evolution in technology and infrastructure. While designed for today's roads, self-driving vehicles can benefit significantly from smarter environments—ones where infrastructure communicates with them, offering real-time road condition data and traffic intelligence. This coordinated network enhances safety and efficiency, preventing disruptions before they occur.
Urban planning must evolve in tandem, considering reduced car ownership's impact—redirecting vast parking spaces to community-beneficial uses like green spaces or housing, creating livable cities. However, this transformation won't occur overnight, demanding adaptive regulations and public education to navigate the hybrid environment of human-driven and autonomous vehicles.
Navigating the Challenges: Hurdles on the Road to Autonomy
While the prospect of autonomous transport is alluring, significant obstacles lie in the path of its widespread adoption. Addressing these complexities, spanning technology, economics, and public sentiment, is crucial for successful integration.
The Technological Puzzle
The intricacy of developing reliable self-navigating systems in diverse real-world environments poses a monumental challenge. These vehicles rely on impeccable sensory and computational capabilities. Despite their sophistication, they must handle an infinite array of unexpected scenarios under varying conditions—ensuring flawless operation in rainfall, amidst dense fog, or in unmarked intersections remains crucial.
Moreover, these systems must interpret vast data swathes, making split-second decisions. Building robust, efficient computing systems capable of this real-time processing is daunting, covering edge cases as varied as a child darting across a street.
The Economic Equation
Autonomous technology involves substantial financial costs. The complex hardware and software systems required are expensive, impacting consumer affordability. Lowering these costs is essential for mainstream adoption—a process requiring time and scale.
Furthermore, economic models for autonomous driving, like taxi services, must overcome high maintenance demands for sensitive equipment. Potential users weigh the convenience and safety of such systems against their significant premiums. Adoption rates for advanced driver-assistance systems suggest skepticism remains about their essential value.
The Human Element: Trust and Acceptance
Trust forms the cornerstone of autonomous adoption. For humans, surrendering control, especially at speed, is daunting. Incidents involving autonomous systems invite scrutiny, potentially eroding public confidence. Building trust requires proven safety records and regulating body assurance.
Optimistic timelines can create mismatches between public expectations and reality. Comprehensive education and transparency about system capabilities are necessary to foster understanding and acceptance—ensuring users feel safe in a vehicle-driven world.
The Foundation: Infrastructure and Regulation
Integrating autonomous vehicles necessitates adapting our current infrastructure, optimized for human drivers. Overhauls, like creating machine-readable smart roads, incur costs while the regulatory framework lags behind technological advancement. Answering complex legal questions and establishing consistent national standards remain imperative to facilitate innovation and secure public comfort amidst change.
Safety First: Addressing Myths and Realities in Autonomous Technology
Autonomous vehicles face scrutiny regarding their safety and security. Debunking pervasive myths emphasizes the efforts behind ensuring reliable operations and public trust.
Addressing Myths: True Complexity of Automation Safety
Automated systems often appear inherently safer; however, greater complexity introduces new vulnerabilities. Autonomous systems require robust safeguarding across every stage—from manufacturing to road deployment. Potential disruptions pose threats if not diligently managed. The challenge is developing a robust framework ensuring security throughout a vehicle's lifecycle.
Furthermore, as connected systems, these vehicles maintain consistent communication with surrounding environments, creating potential exploitation pathways. True safety stems not from automation alone but from a holistic security approach encompassing supply chain integrity and constant vigilance.
Myth of Infallible Decision-Making
The computational prowess of autonomous systems often leads to misconceptions about their infallibility. Despite their speed and accuracy, these systems can encounter decision-making pitfalls due to flawed data interpretation or unforeseen scenarios. Human oversight remains crucial in ensuring predictable behavior and accountability for systems' limitations.
Recognition of potential system misidentifications or biased decision-making underlines continuous improvement endeavors focused on cross-verifying results and managing errors effectively. Perfect system behavior must be predictable, acknowledging system limitations while implementing robust fail-safes.
Understanding Testing - Continual Vigilance
Autonomous system safety undergoes rigorous testing, but assurance involves continuous adaptation. With dynamic road environments, safety advances necessitate constant simulation and real-world testing. Vehicles must evolve alongside shifting challenges, creating robust long-term safety cultures.
Testing spans a wide array of scenarios, ensuring sensor and process robustness from the outset. Post-sale fleet learning further refines systems, accommodating new parameters like changing traffic patterns, confirming sustained improvements and reliability.
Broadening Security: Internal Reliability and Legal Accountability
Security considerations span beyond preventing external hacks, addressing ethical and legal adherence. Vehicles face complex ethical decision-making under collision scenarios, necessitating transparent, guided responses reflecting societal values—an issue demanding broad consensus.
Building robust legal frameworks addressing accident liability, real-time event reconstruction, and regulatory standards are crucial for establishing trust. A comprehensive security approach encompasses external protection, internal reliability, ethical clarity, and robust legal accountability to foster dependable autonomous mobility.
As the world transitions toward self-driving cars, it's essential to unfold the layers of promises and challenges. This new era in transportation demands nuanced understanding and collaborative advancement to ensure these vehicles attain their transformative potential effectively and equitably.
Q&A
-
What is the future of autonomous cars?
The future of autonomous cars is expected to transform the transportation industry by reducing the need for human drivers, increasing road safety, and enhancing mobility for the elderly and disabled. Advancements in AI, machine learning, and sensor technologies are driving this evolution, with fully autonomous vehicles anticipated to become commonplace in urban environments over the next decade. -
How does self-driving car technology work?
Self-driving car technology utilizes a combination of sensors, cameras, radar, and LIDAR to perceive the vehicle's surroundings. These components gather data, which is processed by onboard AI systems to make real-time driving decisions. The technology involves complex algorithms that enable the vehicle to navigate, detect obstacles, and follow traffic laws autonomously. -
What are the benefits of autonomous cars?
Autonomous cars offer several benefits, including increased safety by reducing human error, lower traffic congestion through optimized driving patterns, and enhanced convenience by freeing up time for passengers. They also have the potential to reduce emissions by improving fuel efficiency and supporting electric vehicle integration. -
How safe are autonomous vehicles?
Autonomous vehicles are designed with multiple layers of safety features, including redundancy systems and fail-safes, to ensure reliability. While they have shown promise in reducing accidents caused by human error, ongoing testing and development are crucial to address edge cases and improve safety standards before widespread adoption. -
What challenges do autonomous vehicles face?
Autonomous vehicles face several challenges, such as regulatory hurdles, public acceptance, and ethical considerations in decision-making. Additionally, technological challenges include perfecting AI algorithms to handle diverse driving scenarios and ensuring robust cybersecurity measures to protect against hacking and data breaches.